O novo algoritmo de pesquisa do Google: BERT
Em 25 de outubro de 2019 o Google nos fez uma promessa:
Vamos compreender as pesquisas melhor do que nunca.
É através da criação de um novo algoritmo de pesquisa, o BERT, que o Google promete revolucionar mais uma vez as pesquisas.
Segundo o release postado em seu blog em inglês, o buscador nos esclarece que eles analisam bilhões de pesquisas todos os dias e 15% destas consultas são aquelas que nunca vimos antes. Por isso, criamos maneiras de retornar resultados para consultas que não podemos prever.
Lançamento Oficial do Bert
Hoje, dia 09 de Dezembro de 2019 o Google anunciou em um tweet que liberou o update em seu algorítimo para 70 línguas diferentes.
Tweet
BERT, our new way for Google Search to better understand language, is now rolling out to over 70 languages worldwide. It initially launched in Oct. for US English. You can read more about BERT below & a full list of languages is in this thread…. https://t.co/NuKVdg6HYM
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) December 9, 2019
Pessoas como eu e você usamos pesquisas. Todos os dias. Mas nem sempre temos certeza do que procuramos, ou como procurar.
A essência da pesquisa é a compreensão da linguagem.
Muitas das vezes temos certo o que queremos, mas não temos certeza absoluta das palavras que nos levam até o resultado que precisamos. Isso porque os buscadores precisam das perguntas feitas a sua maneira para nos entregar o que queremos.
É isso que o BERT visa mudar!
Conforme as ferramentas de busca foram evoluindo, principalmente a do Google, ficou ainda mais evidente como algumas coisas ainda não funcionam bem.
As pessoas ainda se sentem obrigas a fazer buscas do ponto de vista do algoritmo, tentando entender como o buscador irá entender o que eles querem achar, ao invés de fazer perguntas do jeito que um ser humano faz a outro.
O problema que o BERT quer resolver
Para resolver esse problema a empresa está fazendo uma melhoria significativa na maneira como eles entendem as consultas, representando o maior salto em frente nos últimos cinco anos e um dos os maiores saltos adiante na história da Pesquisa.
Os últimos avanços da equipe de pesquisa do Google, na ciência do entendimento de idiomas, possibilitada pelo aprendizado de máquina, nos indicam que os resultados futuros serão incríveis.
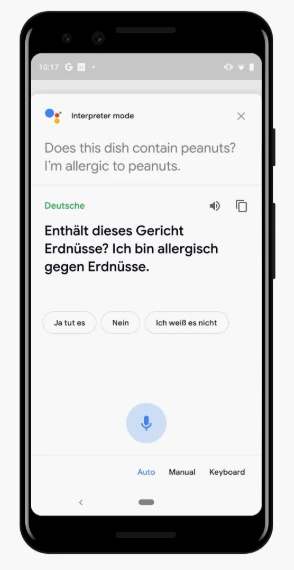
Quer um exemplo?
O Google Tradutor com a ajuda do Google Assistant agora pode traduzir a fala, em tempo real, direto do seu telefone. Chamado de Interpreter Mode, essa funcionalidade chega para facilitar a conversação entre pessoas falantes de línguas diferentes.
Entre em cena o BERT
Um dos maiores desafios no processamento de linguagem natural (PNL) é a falta de dados de treinamento para processar a nossa linguagem de forma a resolver o problema da busca.
Como a PNL é um campo diversificado com muitas tarefas distintas, a maioria dos conjuntos de dados específicos contém apenas alguns milhares (ou algumas centenas de milhares) de exemplos de treinamento rotulados por humanos.

Processamento de linguagem natural no Google BERT
Os modelos modernos de Programação de Linguagem Natural, baseados em aprendizado profundo, demonstram bons resultados quando providos por grandes quantidades de dados.
Eles melhoram quando são treinados usando milhões (ou bilhões) de exemplos de treinamento anotados.
Treinando modelos de aprendizado para melhorar as buscas
Para ajudar a preencher essa lacuna, com os melhores dados, os pesquisadores desenvolveram uma variedade de técnicas para treinar modelos de representação de linguagem de uso geral, usando a enorme quantidade de texto não anotado na Web.
Esta técnica é conhecida como como pré-treinamento.
O modelo pré-treinado pode ser ajustado, durante o processo de aprendizado em PNL com uma amostra pequena de dados.
Esse treinamento tem como resposta as perguntas e análises de sentimentos, melhorias substanciais de precisão em comparação com o treinamento nesses conjuntos de dados a partir do zero.
Essa tecnologia permite que qualquer pessoa treine seu próprio sistema de atendimento de perguntas de última geração, abrindo possibilidades de novos negócios a muitas empresas, de todos os tamanhos.
Transforme, o novo modelo de aprendizagem de linguagem
Transformer, usa um novo modelo de rede neural para entender o significado das frases.
Já não usa critérios como tamanho das palavras mas modelos que processam palavras em relação a todas as outras palavras em uma frase, em vez de uma por uma na ordem.
A semântica, por tanto, é cada vez mais fundamental no entendimento dos algorítimos do Google.
Os modelos BERT podem, portanto, considerar o contexto completo de uma palavra observando as palavras que vêm antes e depois dela – particularmente útil para entender a intenção por trás das consultas de pesquisa.
Quebrando o código das buscas
A pesquisa dos buscadores atuais poderão entender o contexto das palavras na sua consulta, usando o tecnologias como o BERT.
Você vai poder pesquisar de uma maneira cada vez mais natural para você.
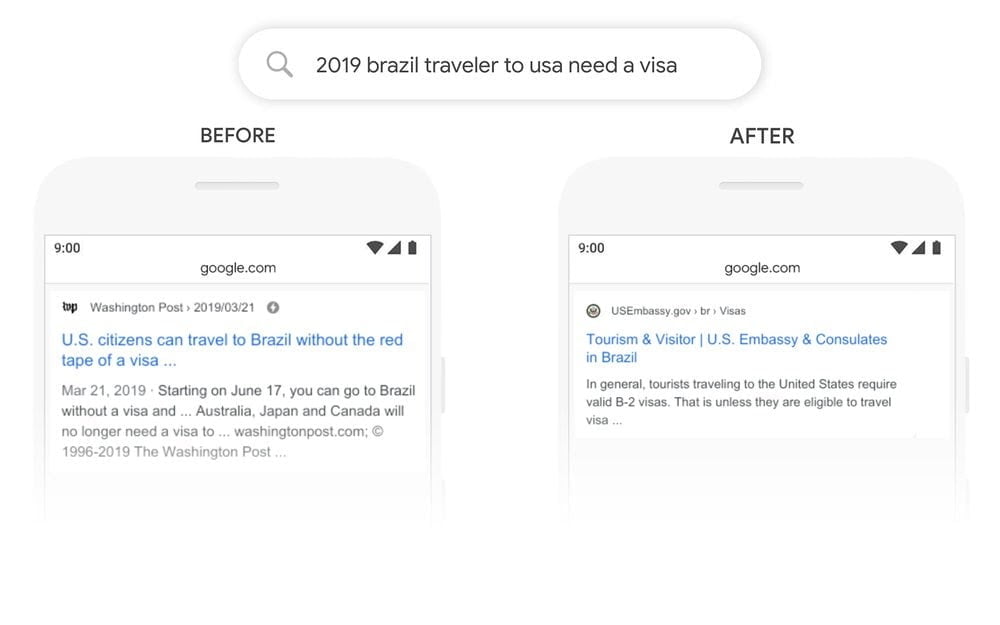
O Google mesmo explicou a nossa busca, turbinada pelo BERT:
Antes a palavra “to” nessa busca em inglês era levada pouco em consideração por ser um termo muito usado, comum. E por isso o resultado mostrado não era preciso para a pergunta: “se em 2019 um brasileiro em viagem aos EUA precisa de visto”.
Depois dessa implementação o algoritmo já entende que a preposição é extremamente importante, por ser ele é que dá sentido a pergunta.
Em resumo, palavras críticas vão ser levadas muito mais em questão a partir dessa implementação no algoritmo.
Melhorando a pesquisa em mais idiomas
Para os snippets em destaque, o Google está usando um modelo BERT para melhorar os snippets em destaque nas duas dúzias de países em que esse recurso está disponível.
Analisando esses resultados já é possível observar melhorias significativas em idiomas como coreano, hindi e o nosso português.
Como os usuários compreendem os resultados das buscas?
SERPs complexas alteram o comportamento dos usuários perante as pesquisa, e a surge: o padrão de pinball. Para entender o padrão pinball, leia esse estudo do Nielsen Norman Group por Kate Moran and Cami Goray.
O conteúdo complexo e dinâmico nas páginas de resultados – SERPs – recebe muita atenção por parte dos buscadores. Quando esses recursos estão presentes, como os trechos em destaque, na página de resultados, os pesquisadores do Google descobriram que eles receberam atenção dos usuários em 74% dos casos.
Como as páginas de resultados de pesquisa agora não mostram padrões iguais, de consulta para consulta, os usuários geralmente são forçados a avaliar a página antes de se aprofundar e fazer um clique em algo.
Isso significa que o layout de uma SERP pode determinar quais links obtêm visibilidade e quais são clicados.
A inconsistência das SERPs
A inconsistência no layout das SERPs significa que os usuários trabalham mais para processar as informações hoje, do que costumavam fazer anteriormente.
Podemos dizer que os mecanismos de pesquisa estão nos incentivando a explorar mais as páginas com o resultado das nossas buscas, indo além do primeiro resultado. No entanto, as pessoas são bastante rápidas na escolha de um resultado de pesquisa – descobrimos que os usuários gastaram uma média de 5,7 segundos considerando os resultados antes de fazer sua primeira seleção (com um intervalo de confiança de 95% de 4,9 a 6,5 segundos).
Você nem sempre precisa ser o primeiro
O que esse novo padrão de olhar significa para equipes de produtos digitais e criadores de conteúdo?
Em 2006, o primeiro resultado em qualquer página de resultados recebeu 51% dos cliques. Em nosso projeto, ao contrário, descobrimos que a primeira posição em uma SERP (definida como o primeiro item listado na caixa de pesquisa) recebia apenas 28% dos cliques – quase metade, o que é uma mudança drástica no comportamento do usuário em pouco tempo. de apenas cerca de uma década. 59% dos cliques foram concentrados nas três primeiras posições, mas as posições inferiores receberam um pouco mais de cliques do que em 2006.
Quando as páginas de resultados de pesquisa contêm elementos complexos e visualmente atraentes, é mais provável que os usuários sejam atraídos para esses elementos e distribuam sua atenção pelo SERP.
Se você conseguir chegar às 5 primeiras posições em uma SERP, terá uma boa chance (40 a 80%) de obter uma visão valiosa do seu usuário.
Ainda é importante aparecer na primeira página de resultados, pois é provável que as pessoas não cliquem na segunda página.
Considere adicionar alguns desses recursos SERP não tradicionais à sua pesquisa no site, se isso fizer sentido para o seu conteúdo. Mas lembre-se de que quando as páginas de resultados são muito inconsistentes de consulta para consulta, os usuários precisam reavaliar a página a cada vez, o que aumenta o custo da interação.
Fonte: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/pinball-pattern-search-behavior/
Perguntas Frequentes
O que é algoritmo?
Em ciência da computação, um algoritmo é uma sequência finita de ações executáveis que visam obter uma solução para um determinado tipo de problema. Segundo Dasgupta, Papadimitriou e Vazirani, “algoritmos são procedimentos precisos, não ambíguos, mecânicos, eficientes e corretos”
O que é processamento de linguagem natural?
Processamento de linguagem natural ou PNL é uma subárea da ciência da computação, inteligência artificial e da linguística que estuda os problemas da geração e compreensão automática de línguas humanas naturais.




Publicar comentário